Title Image by JBStuka
For decades after dinosaurs were discovered, people thought they were just big, dumb, plodding animals. One of the discoveries that helped convince scientists that there was much more to dinosaurs than that was the discovery of Maiasaura.

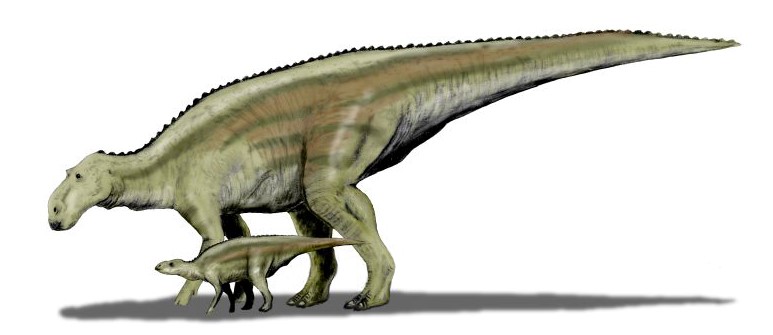
Fernando Losada Rodríguez, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
In 1978, paleontologist, Jack Horner, discovered a field of dinosaur nests in Montana. The nests not only had unhatched dinosaur eggs but also skeletons of baby dinosaurs. The babies were not newborns. They were too big to have just hatched. That meant they were living in the nest — which meant the mother dinosaurs were taking care of the babies! If the babies had to feed themselves, they would have wandered away from the nest. This was an amazing idea at the time. No one thought dinosaurs were smart enough to take care of their babies. Horner named the dinosaur Maiasaura, which means “good mother lizard.”
In many ways, Maiasaura was just an average dinosaur, which makes their caretaking even more interesting. It is one of the duckbilled dinosaurs. Duckbilled is a nickname given to several different types of dinosaurs that had mouths shaped like a duck’s bill. The Maiasaura didn’t have any teeth in the front of its long, flat mouth, but in its cheeks, it had hundreds of them.
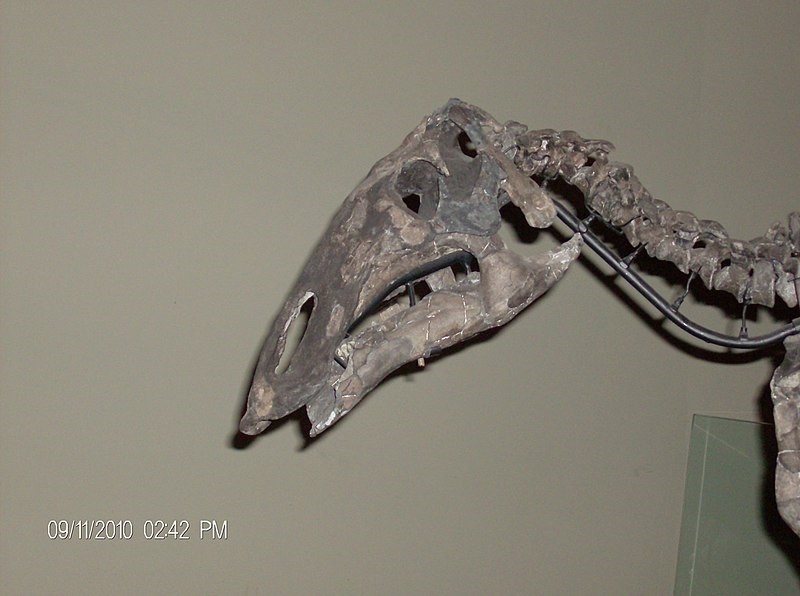

Many duckbilled dinosaurs had fancy crests on their heads, but the Maiasaura’s head was flat, with just a very short, bony spike above its eyes. Some scientists think the Maiasaura might have had a flap of skin, like the comb of a rooster, attached to the spike. Male Maiasauras could have used that to attract the attention of female Maiasauras.
A Maiasaura was about the size of a camping trailer. That may sound big, but it was only average for a dinosaur. Most adult Maiasauras grew about 20 feet long. They stood about 15 feet high and weighed about two-and-a-half tons.
Maiasauras walked on all four legs much of the time, but they could walk on just their two back legs if they needed to. Their front legs were smaller and thinner than their back legs and had four fingers.

The Maiasaura was a plant-eating dinosaur. It ate tree needles, twigs, seeds and berries. As you might expect, chewing these tough, woody foods wore its teeth down. But the Maiasaura had an easy way to avoid the dentist. It had teeth stacked inside its jaws, one on top of the other. Whenever a tooth wore out, it just fell out and was replaced by the one underneath.
All dinosaurs hatched from eggs. The Maiasaura laid her eggs in bowl-shaped nests. As you might guess, these big creatures needed BIG nests – about six-feet wide! Scientists think the mothers used their powerful back legs to make a huge mound of dirt on a flat area and used their arms to hollow out the center. Many Maiasauras made their nests in the same area, keeping them about 23 feet apart. That allowed the mothers space to walk between the nests without stepping on anyone else’s nest. The mothers probably brought plants to the nest to cover the eggs to keep them warm. If they had sat on them, they would have squashed them!
The babies were about 14 inches long when they were born – about the size of one of their mother’s feet. Each weighed only three or four pounds. The mother brought food to the nest, just as a mother bird will do today. We know the babies stayed at least part of the time in the nest because the shells in the nest were broken into tiny pieces as if walked over many times. Some of the baby skeletons Horner found in the nests were about three feet long. It probably took them several months to grow that big, so an adult must have not only brought them food all that time, but also guarded them from meat-eating dinosaurs looking for a snack.

When the babies were big enough, they joined a herd. Huge herds of Maiasauras roamed the upper coastal plains – as many as 10,000 in a single herd! This was their best defense against predators. Meat eaters would have to look for a single dinosaur that became separated from the herd. Maiasauras had good hearing and good eyesight, so they could be aware of danger. They would eat all the plants in one place and then move on to another. Scientists think they may have traveled a regular route, always returning to the same nesting ground when it was time to lay their eggs.
Over the years many paleontologists have returned to what they call “Egg Mountain” in Montana to study the bones, eggs, and nests fossilized there. The more they learn, the more amazing this “good mother” dinosaur seems.
Sources (Click me!)
Gaur, Aakanksha. “Maiasaura.” Britannica. 6 December 2019. https://www.britannica.com/ animal/Maiasaura
Horner, John R. and James Gorman. Maia: A Dinosaur Grows Up. Running Press, 1987. “Largest dinosaur population growth study ever shows how Maiasaura lived and died.” Montana State University News Service. 1 October 2015. https://www.montana.edu/news/15769/largest-dinosaur-population-growth-study-ever-shows-how-maiasaura-lived-and-died
Okoyomon, Adesuwa. “Meet Maiasaura, the Good Mother Lizard.” Science World. 12 July 2022. https://www.scienceworld.ca/stories/maiasaura-good-mother-lizard/
Riehecky, Janet. Maiasara. The Child’s World, 1989.

So very interesting. The details of how these dinosaurs lived makes it easy to imagine them in great herds like the modern day African animals.
LikeLiked by 1 person
As always, another good article!
LikeLike
Great story! Love how you shared the ways they figured this out.
LikeLike
Wow. I never knew so much could be derived from that little detail.
LikeLike